2D‐3D registration is challenging in the presence of implant projections on intraoperative images, which can limit the registration capture range. Here, we investigate the use of deep‐learning‐based inpainting for removing implant projections from the X‐rays to improve the registration performance.
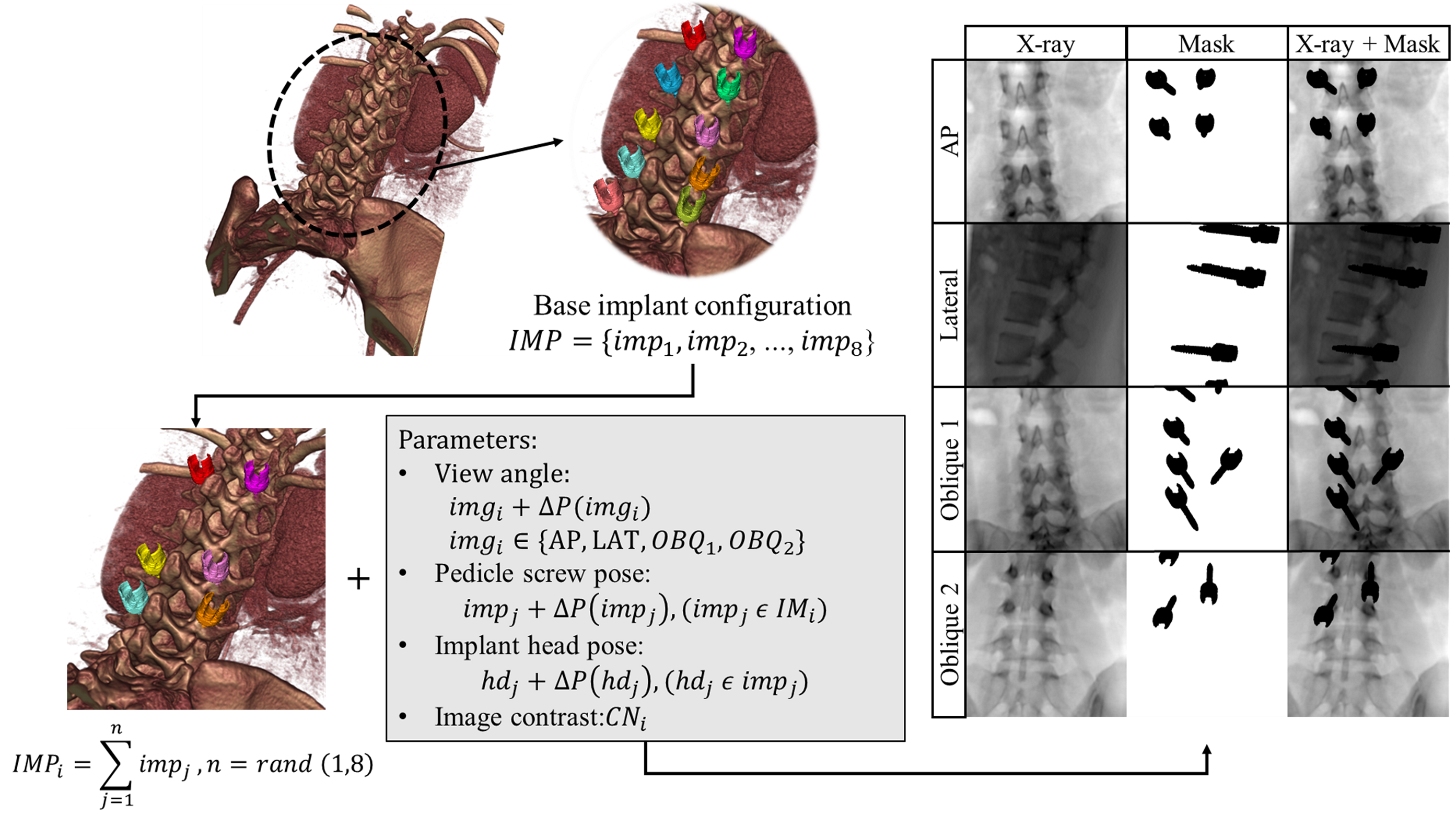
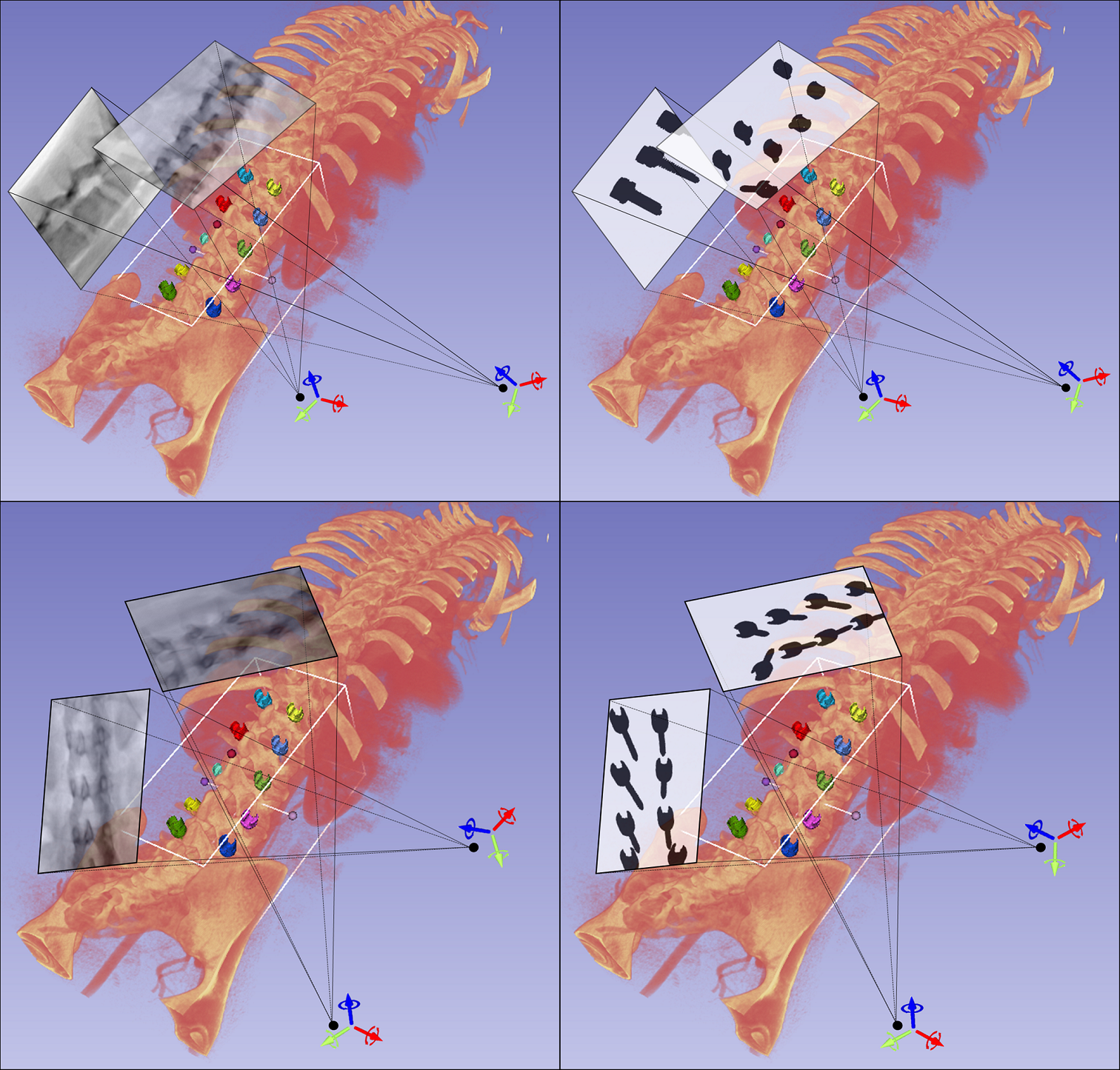
We trained deep‐learning‐based inpainting models that can fill in the implant projections on X‐rays. Clinical datasets were collected to evaluate the inpainting based on six image similarity measures. The effect of X‐ray inpainting on capture range of 2D‐3D registration was also evaluated.
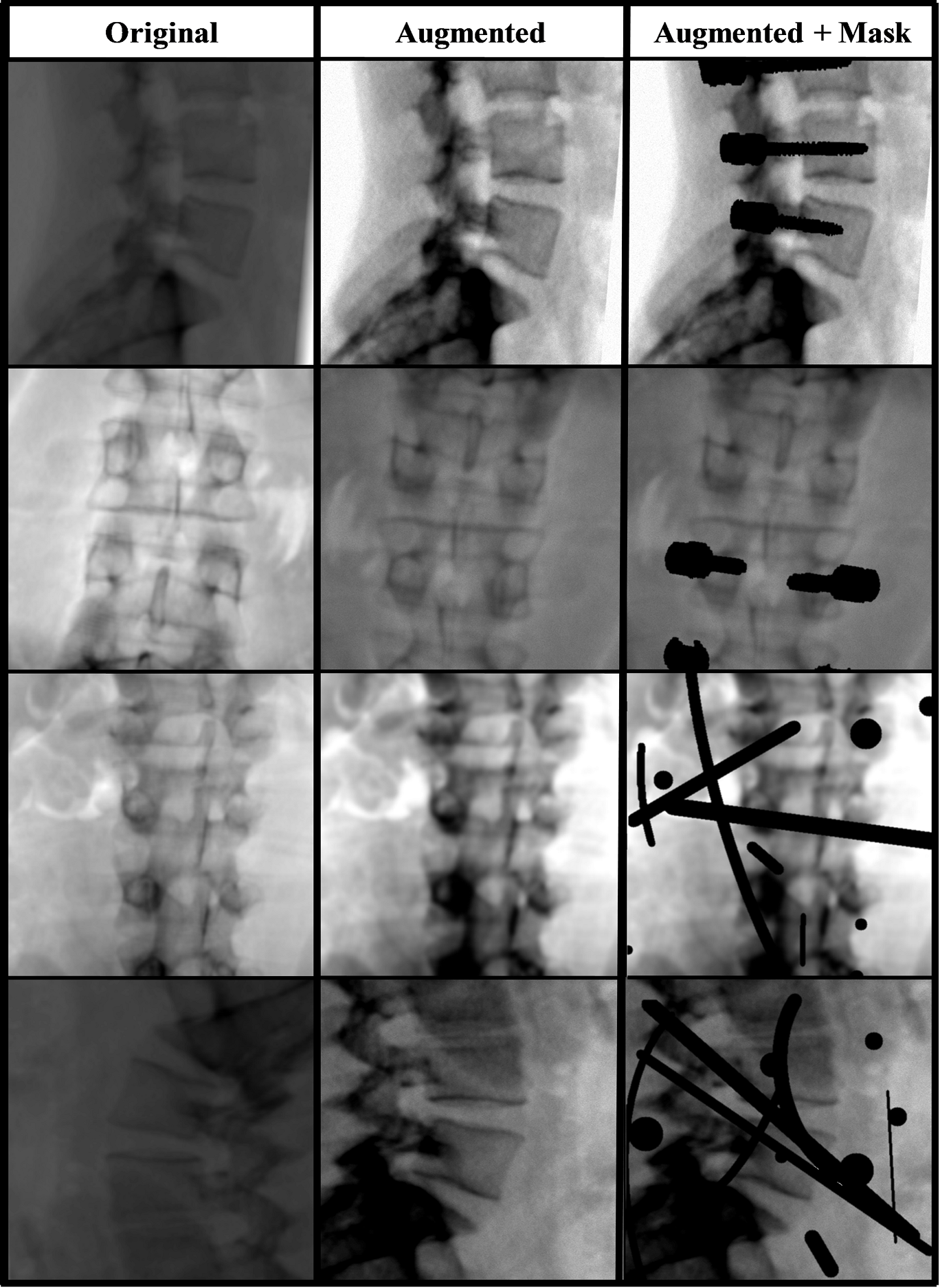
The X‐ray inpainting significantly improved the similarity between the inpainted images and the ground truth. When applying inpainting before the 2D‐3D registration process, we demonstrated significant recovery of the capture range by up to 85%. Applying deep‐learning‐based inpainting on X‐ray images masked by implants can markedly improve the capture range of the associated 2D‐3D registration task
Such an approach will likely have significant value both in our target application of intraoperatively estimating the pose of pedicle screws during spine surgery and in a range of related applications (e.g., orthopaedic trauma) in which similar registration processes are required. In addition, we anticipate potential benefits in applications where one wishes to remove image artefacts, such as removing metal artefacts on cone‐beam CT volumes.
Citation
Esfandiari H, Weidert S, Kövesházi I, Anglin C, Street J, Hodgson AJ.
Deep learning-based X-ray inpainting for improving spinal 2D-3D registration.
Int J Med Robot. 2021 Apr;17(2):e2228.